Tuberculosis (TB) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis primarily attacks the lungs, though it may affect other organs such as the kidneys, spine, and brain, whose signs and symptoms vary depending on the organs involved. For example, Tuberculosis affecting the spine can cause back pain, while Tuberculosis of the kidneys may lead to blood in the urine.
TB contributes to leading cases of deaths worldwide, while India records the highest TB burden incidence, with over 2.4 million active TB cases reported by the WHO in 2019. To raise public awareness about the global tuberculosis epidemic and collaborate towards disease eradication, 24th March is observed as the World Tuberculosis Day worldwide.
Types of TB
Tuberculosis (TB) can be an active TB, miliary TB or a latent TB infection, discussed below-
- Active TB– Active tuberculosis (TB) is the most common type of tuberculosis, characterized by the rapid multiplication of the TB bacterium and subsequent invasion of various organs of the body. Weight loss, fever, chills, night sweats, cough, phlegm, chest pain, and fatigue are all symptoms of active tuberculosis.
- Miliary TB– A rare form of tuberculosis. It occurs when the tuberculosis bacteria enter the bloodstream and quickly spread throughout the body in tiny nodules, affecting multiple organs at the same time.
- Latent TB– Those diagnosed with latent TB may not develop initial symptoms, with their X-ray results showing normal assessments. However, it would be only after an interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) or an advanced tuberculin skin test (TST) that would detect latent TB. In some cases, a latent infection may slowly advance to the common and potentially dangerous active TB.
Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Dangers of TB
| Symptoms of TB | Risk Factors of TB (Factors that may complicate TB) | Dangers of TB (TB complications) |
| Coughing over three or more weeks | HIV or AIDS | Joint damage |
| Coughing up blood | Diabetes | Lung damage |
| Chest pain, or pain while breathing | Severe kidney disease | Bone, spinal cord, brain, or lymph nodes infection and damage |
| Unexplained weight loss | Head and neck cancers | Liver or kidney problems |
| Fatigue | Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy | Inflammation of the tissues around the heart |
| Fever | Low body weight and poor nutrition | |
| Night sweats | Organ transplant medications | |
| Chills | Medications that treat rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis | |
| Loss of appetite | Smoking |
Tuberculosis Transmission
When TB carriers cough, sneeze or talk without a facemask, they release tiny droplets that carry germs and the contagious Tuberculosis Bacteria. However, TB is not easy to catch; one has to spend a considerable amount of time around a TB patient to get infected.
Interestingly, Tuberculosis germs do not survive for a long time on surfaces. Besides, you will not catch TB from shaking hands or sharing food with a TB-infected person.
Bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) Vaccination
The relatively safe and readily available BCG (Bacillus Calmette–Guérin) vaccine, protects against tuberculosis (TB).
Notably, not every country administers the BCG vaccine. However, in countries where tuberculosis or leprosy cases are common, like India, one dose of the BCG vaccine is given to new-born babies as soon as they are born. This one dose provides lifelong immunity against TB.
When to see a doctor
Though fever, unexplained weight loss, drenching night sweats, or persistent cough might be shrugged off as stress fatigue, you must not ignore them. These may be warning signs though they may also indicate other medical problems. Reach out to a doctor on the Gigadocs E- healthcare app and discuss your symptoms to let your doctor determine the cause.
People who use IV drugs or are in contact with TB infected individuals or are living in areas where TB incidents are common, like the states of Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Himachal Pradesh, need to be cautious of TB risk exposure.
Tuberculosis Diagnosis with Gigadocs
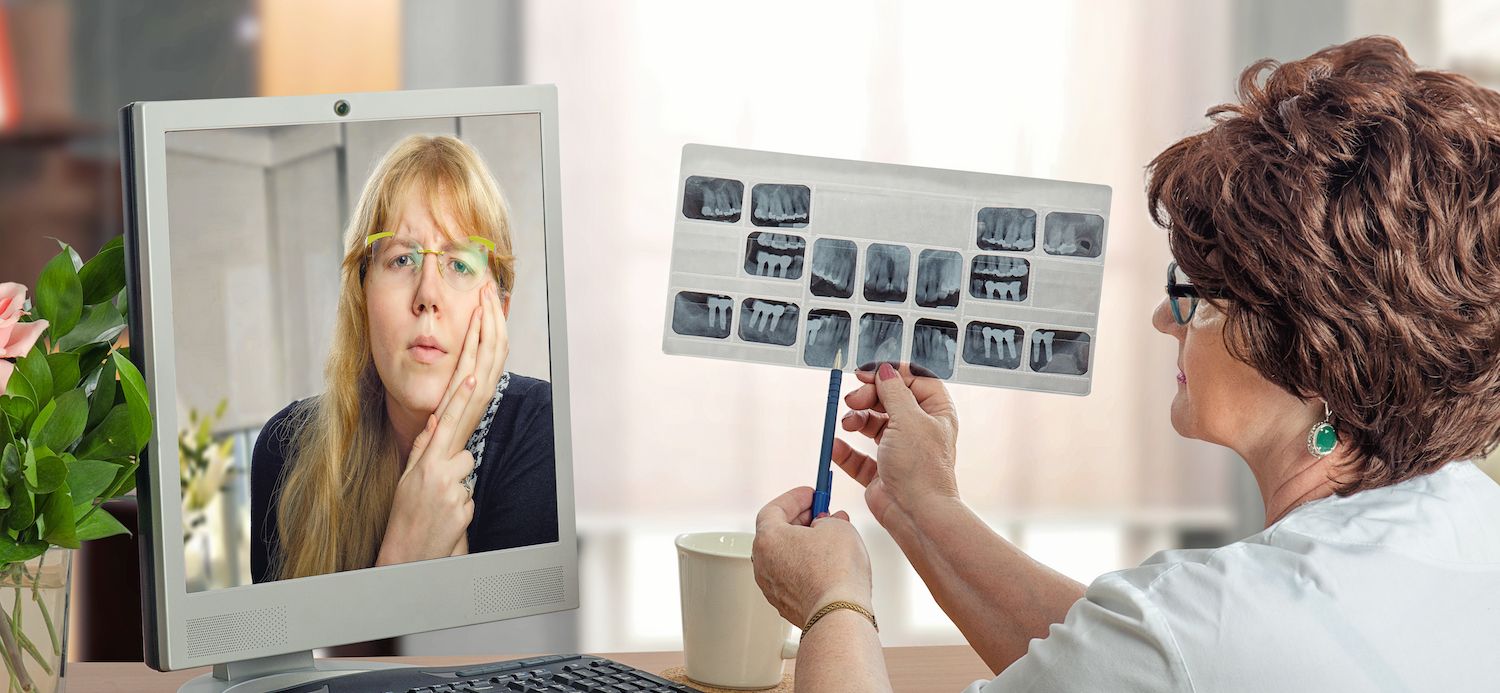
For an accurate TB diagnosis, your doctor will prescribe two common tests that includes the Mantoux tuberculin skin test and the interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs). Your doctor may also ask for a chest X-ray or CT scan and an Acid-fast bacillus (AFB) test.
To know more about these tests, and to consult a doctor near you or within the privacy of your home, download the Gigadocs app from the App/ Play store.
Gigadocs offers Chronic Disease Consultation online and offline, Healthcare Management, Patient record safekeeping, all integrated into one interactive app.
To download Gigadocs app-
- IOS App – apple.co/2W2iG4V
- Android App – bit.ly/33AQoRC
To know more and schedule a demo, e-mail, at info@gigadocs.com